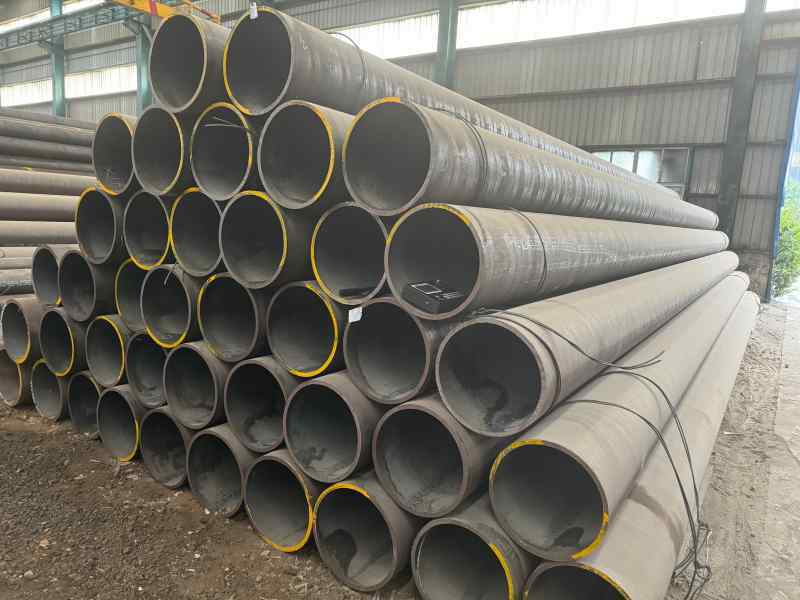
alloy steel tubes seamless pipes 34CrNiMo6 30CrNiMo8
Category:
Steel Tube
Brief description:
alloy steel tubes seamless pipes 34CrNiMo6 30CrNiMo8
Key words:
Product Description
Product Description
Table 1— Steel grades and chemical composition (cast analysis)
Chemical composition % by mass( a,b)
|
Steeldesignation Name |
C
|
Si max.
|
Mn
|
P max.
|
S
|
Cr
|
Mo
|
Ni
|
V
|
B
|
|
34CrMo4 |
0,30 to 0.37
|
0,40
|
0,60 to 0,90
|
0,025
|
max. 0,035
|
0,90to 1,20 0,035 0,90 to 1,20
|
0,15 to 0,30
|
- |
- -- |
|
|
34CrMoS4 |
0,30 to 0.37
|
0,40
|
0,60 to 0,90
|
0,025
|
max. 0,035
|
0,90 to 1,20
|
0,15 to 0,30
|
- |
- -- |
- - |
|
42CrMo4 |
0,38 to 0,45
|
0,40
|
0,60 to 0,90
|
0,025
|
max. 0,035
|
0,90 to 1,20
|
0,15 to 0,30
|
- |
- -- |
- - |
|
42CrMoS4 |
0,38 to 0,45
|
0,40
|
0,60 to 0,90
|
0,025
|
0,020 to 0,040
|
0,90 to 1,20
|
0,15 to 0,30
|
- |
- -- |
- - |
|
34CrNiMo6 |
0,30 to 0,38
|
0,40
|
0,50 to 0,80
|
0,025
|
max. 0,035
|
1,30 to 1,70
|
0,15 to 0,30
|
1,30to1,70
|
- -- |
- - |
|
30CrNiMo8 |
0,26 to 0,34
|
0,40
|
0,50 to 0,80
|
0,025
|
max. 0,035
|
1,80 to 2,20
|
0,30 to 0,50
|
1,80 to 2,20
|
- |
- |
|
a.Elements not quoted in this table shall not be intentionally added to the steel without the agreement of the purchaser, other than for the purpose of finishing the heat and for boron to have its effect on the hardenability. All reasonable precautions shall be taken to prevent the addition of such elements from scrap or other material used in the manufacture which affect the hardenability, mechanical properties and applicability. |
||||||||||
|
B.Where requirements are made on hardenability (see Tables 5 and 6) or on the mechanical properties in the quenched and tempered condition (see Table 8), slight deviations from the limits for the cast analysis are permissible, except for the elements carbon, phosphorus and sulfur; the deviations shall not exceed the specifications of Table 4. C.Steels with improved machinability as a result of the addition of higher sulphur contents up to around 0,10% S (including resulphurized steels with controlled inclusion content (e.g. Ca-treatment)) may be supplied on request. In this case the upper limit for the manganese content may be increased by 0,15 %. |
||||||||||
Table 2— Limiting values for the "C" scale Rockwell hardness for special steel grades with (normal) hardenability requirements
(+H grades)
| Steel designation | Symbol | Limits of | Distance in mm from quenched end | |||||||||||||||
| Name | range | Hardness in HRC | ||||||||||||||||
| 1.5 | 3 | 5 | 7 | 9 | 11 | 13 | 15 | 20 | 25 | 30 | 35 | 40 | 45 | 50 | ||||
| Steels without boron | ||||||||||||||||||
| 34CrMo4 | +H | max | 57 | 57 | 57 | 56 | 55 | 54 | 53 | 52 | 48 | 45 | 43 | 41 | 40 | 40 | 39 | |
| 34CrMoS4 | +H | min | 49 | 49 | 48 | 45 | 42 | 39 | 36 | 34 | 30 | 28 | 27 | 26 | 25 | 24 | 24 | |
| 42CrMo4 | +H | max | 61 | 61 | 61 | 60 | 60 | 59 | 59 | 58 | 56 | 53 | 51 | 48 | 47 | 46 | 45 | |
| 42CrMoS4 | +H | min | 53 | 53 | 52 | 51 | 49 | 43 | 40 | 37 | 34 | 32 | 31 | 30 | 30 | 29 | 29 | |
| 34CrNiMo6 | +H | max | 58 | 58 | 58 | 58 | 57 | 57 | 57 | 57 | 57 | 57 | 57 | 57 | 57 | 57 | 57 | |
| min | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 49 | 48 | 48 | 48 | 48 | 47 | 47 | 47 | 46 | 45 | 44 | |||
| 30CrNiMo8 | +H | max | 56 | 56 | 56 | 56 | 55 | 55 | 55 | 55 | 55 | 54 | 54 | 54 | 54 | 54 | 54 | |
| min | 48 | 48 | 48 | 48 | 47 | 47 | 47 | 46 | 46 | 45 | 45 | 44 | 44 | 43 | 43 | |||
Table 3— Limiting values for the C scale Rockwell hardness for special steel grades with restricted hardenability scatter bands
(+HH and +HL grades)
| Steel designation | Symbol | Limits of | Distance in mm from quenched end | |||||||||||||||
| Name | range | Hardness in HRC | ||||||||||||||||
| 1.5 | 3 | 5 | 7 | 9 | 11 | 13 | 15 | 20 | 25 | 30 | 35 | 40 | 45 | 50 | ||||
| Steels without boron | ||||||||||||||||||
| 34CrMo4 | +HH | max | 57 | 57 | 57 | 56 | 55 | 54 | 53 | 52 | 48 | 45 | 43 | 41 | 40 | 40 | 39 | |
| min | 52 | 52 | 51 | 49 | 46 | 44 | 42 | 40 | 36 | 34 | 32 | 31 | 30 | 29 | 29 | |||
| 34CrMoS4 | +HL | max | 54 | 54 | 54 | 52 | 51 | 49 | 47 | 46 | 42 | 39 | 38 | 36 | 35 | 35 | 34 | |
| min | 49 | 49 | 48 | 45 | 42 | 39 | 36 | 34 | 30 | 28 | 27 | 26 | 25 | 24 | 24 | |||
| 42CrMo4 | +HH | max | 61 | 61 | 61 | 60 | 60 | 59 | 59 | 58 | 56 | 53 | 51 | 48 | 47 | 46 | 45 | |
| min | 56 | 56 | 55 | 54 | 52 | 48 | 46 | 44 | 41 | 39 | 38 | 36 | 36 | 35 | 34 | |||
| 42CrMoS4 | +HL | max | 58 | 58 | 58 | 57 | 56 | 54 | 53 | 51 | 49 | 46 | 44 | 42 | 41 | 40 | 40 | |
| min | 53 | 53 | 52 | 51 | 49 | 43 | 40 | 37 | 34 | 32 | 31 | 30 | 30 | 29 | 29 | |||
| 34CrNiMo6 | +HH | max | 58 | 58 | 58 | 58 | 57 | 57 | 57 | 57 | 57 | 57 | 57 | 57 | 57 | 57 | 57 | |
| min | 53 | 53 | 53 | 53 | 52 | 51 | 51 | 51 | 51 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 49 | 48 | |||
| +HL | max | 55 | 55 | 55 | 55 | 54 | 54 | 54 | 54 | 54 | 54 | 54 | 54 | 53 | 53 | 53 | ||
| min | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 49 | 48 | 48 | 48 | 48 | 47 | 47 | 47 | 46 | 45 | 44 | |||
| 30CrNiMo8 | +HH | max | 56 | 56 | 56 | 56 | 55 | 55 | 55 | 55 | 55 | 54 | 54 | 54 | 54 | 54 | 54 | |
| min | 51 | 51 | 51 | 51 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 49 | 49 | 48 | 48 | 47 | 47 | 47 | 47 | |||
| +HL | max | 53 | 53 | 53 | 52 | 52 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 48 | 48 | 45 | 45 | - | - | - | ||
| min | 48 | 48 | 48 | 48 | 47 | 47 | 47 | 46 | 46 | 45 | 45 | 44 | 44 | 43 | 43 | |||
Table 4— Maximum hardness for products to be supplied in the "treated to improve shearability (+S)"
or "soft annealed (+A)" condition
|
Steel designationa Name |
Max. HBW in conditionb
|
|
|
|
+S |
+A |
|
34CrMo4,34CrMoS4 |
255c |
223 |
|
|
|
|
|
42CrMo4,42CrMoS4 |
255c |
241 |
|
|
|
|
|
34CrNiMo6 |
-d |
248 |
|
30CrNiMo8 |
-d |
248 |
|
aThe values apply also for the steel with hardenability requirements (+H-, +HH- and +HL-grades) covered in Tables 5 and 6; see, however, footnote c. |
||
|
bThe values are not applicable to slabs which have been continuously cast and not further deformed. cDepending on the chemical composition of the cast, and on the dimensions, particularly in the case of the +HH-grades, soft annealing may be necessary. |
||
|
dWhere the shearability is of importance, this steel should be ordered in the "soft-annealed" condition. |
||
|
eShearable in the untreated condition. |
||
|
fCondition +A is not applicable for boron steels. |
||
Table 5— Mechanical properties aat room temperature in the quenched and tempered condition (+QT)
|
Steel designation Name |
Mechanical properties for the ruling section (see EN 10083-1:2006, Annex A) with a diameter (d) or for flat products thickness (t) of |
||||
|
d≤ 16 mm ,t≤ 8 mm |
|||||
|
|
Remin. |
Rm |
Amin |
Z min |
KVbmin |
|
|
MPac |
MPac |
% |
% |
J |
|
34CrMo4 |
800 |
1000-1200 |
11 |
45 |
- |
|
34CrMoS4 |
800 |
1000-1200 |
11 |
45 |
- |
|
42CrMo4 |
900 |
1100-1300 |
10 |
40 |
- |
|
42CrMoS4 |
900 |
1100-1300 |
10 |
40 |
- |
|
34CrNiMo6 |
1000 |
1200-1400 |
9 |
40 |
- |
|
30CrNiMo8 |
1050 |
1250-1450 |
9 |
40 |
- |
|
Steel designation Name |
Mechanical properties for the ruling section (see EN 10083-1:2006, Annex A) with a diameter (d) or for flat products thickness (t) of |
||||
|
16 mm < d≤ 40 mm ,8 mm < t≤ 20 mm |
|||||
|
|
Remin. |
Rm |
Amin |
Z min |
KVbmin |
|
|
MPac |
MPac |
% |
% |
J |
|
34CrMo4 |
650 |
900-1000 |
12 |
50 |
40 |
|
34CrMoS4 |
650 |
900-1000 |
12 |
50 |
40 |
|
42CrMo4 |
750 |
1000-1200 |
11 |
45 |
35 |
|
42CrMoS4 |
750 |
1000-1200 |
11 |
45 |
35 |
|
34CrNiMo6 |
900 |
1100-1300 |
10 |
45 |
45 |
|
30CrNiMo8 |
1050 |
1250-1450 |
9 |
40 |
30 |
|
Steel designation Name |
Mechanical properties for the ruling section (see EN 10083-1:2006, Annex A) with a diameter (d) or for flat products thickness (t) of |
||||
|
40 mm < d≤ 100 mm,20 mm < t≤ 60 mm |
|||||
|
|
Remin. |
Rm |
Amin |
Z min |
KVbmin |
|
|
MPac |
MPac |
% |
% |
J |
|
34CrMo4 |
550 |
800-950 |
14 |
55 |
45 |
|
34CrMoS4 |
550 |
800-950 |
14 |
55 |
45 |
|
42CrMo4 |
650 |
900-1100 |
12 |
50 |
35 |
|
42CrMoS4 |
650 |
900-1100 |
12 |
50 |
35 |
|
34CrNiMo6 |
700 |
1000-1200 |
11 |
50 |
45 |
|
30CrNiMo8 |
800 |
1000-1300 |
10 |
45 |
35 |
|
Steel designation Name |
Mechanical properties for the ruling section (see EN 10083-1:2006, Annex A) with a diameter (d) or for flat products thickness (t) of |
||||
|
100 mm < d≤ 160 mm,60 mm < t≤ 100 mm |
|||||
|
|
Remin. |
Rm |
Amin |
Z min |
KVbmin |
|
|
MPac |
MPac |
% |
% |
J |
|
34CrMo4 |
500 |
750-900 |
15 |
55 |
45 |
|
34CrMoS4 |
500 |
750-900 |
15 |
55 |
45 |
|
42CrMo4 |
550 |
800-950 |
13 |
50 |
35 |
|
42CrMoS4 |
550 |
800-950 |
13 |
50 |
35 |
|
34CrNiMo6 |
700 |
900-1000 |
12 |
55 |
45 |
|
30CrNiMo8 |
800 |
1000-1200 |
11 |
50 |
45 |
|
Steel designation Name |
Mechanical properties for the ruling section (see EN 10083-1:2006, Annex A) with a diameter (d) or for flat products thickness (t) of |
||||
|
160 mm < d≤ 250 mm ,100 mm < t≤ 160 mm |
|||||
|
|
Remin. |
Rm |
Amin |
Z min |
KVbmin |
|
|
MPac |
MPac |
% |
% |
J |
|
34CrMo4 |
450 |
700-850 |
15 |
60 |
45 |
|
34CrMoS4 |
450 |
700-850 |
15 |
60 |
45 |
|
42CrMo4 |
500 |
750-900 |
14 |
55 |
35 |
|
42CrMoS4 |
500 |
750-900 |
14 |
55 |
35 |
|
34CrNiMo6 |
600 |
800-950 |
13 |
55 |
45 |
|
30CrNiMo8 |
700 |
900-1100 |
12 |
50 |
45 |
|
a Re: Upper yield strength or, if no yield phenomenon occurs, 0,2 % proof strength Rp0,2. Rm: Tensile strength. A: Percentage elongation after fracture (initial gauge length Lo= 5,65 S0see Table 10, column 7a, line T4). Z: Reduction in cross section on fracture. KV: Impact strength of longitudinal Charpy-V-notch test pieces (average of 3 individual values shall meet the minimum specified in the table; no individual value shall be lower than 70 % of the minimum shown in the table.) |
|||||
|
b.For sampling see EN 10083-1:2006 fig.1 and fig.3 |
|||||
|
c1 MPa = 1 N/mm2. |
|||||
|
dFor 40 mm < d≤ 60 mm and 20 mm < t≤ 40 mm. |
|||||
Table 6— Heat treatment a
|
Steel designationb Name |
Quenching c,d °C |
Quenchinge agent |
Temperingf °C |
End quench test °C |
|
34CrMo4 |
830 to 890 |
Oil or water |
540 to 680 |
850 ±5 |
|
34CrMoS4 |
830 to 890 |
Oil or water |
540 to 680 |
850 ±5 |
|
42CrMo4 |
820 to 880 |
Oil or water |
540 to 680 |
850 ±5 |
|
42CrMoS4 |
820 to 880 |
Oil or water |
540 to 680 |
850 ±5 |
|
34CrNiMo6 |
830 to 860 |
Oil or water |
540 to 660 |
850 ±5 |
|
30CrNiMo8 |
830 to 860 |
Oil or water |
540 to 660 |
850 ±5 |
|
aThe conditions given in this table are for guidance. However, the temperatures specified for the end quench test are mandatory. |
||||
|
bThis table also applies for the various grades with specified hardenability (+H-, +HH- and +HL grades) covered in Tables 5 and 6. |
||||
|
cThe temperatures at the lower end of the range are generally applicable to hardening in water and those at the upper end for hardening in oil. |
||||
|
dAustenitizing period: at least 30 min (guide value). |
||||
|
eWhen choosing the quenching agent the influence of other parameters, such as shape, dimensions and quenching temperature on properties and crack susceptibility should be taken into account. Other quenching agents such as synthetic quenchants may also be used. |
||||
|
fTempering period: at least 60 min (guide value). |
||||








 +86 866358882101
+86 866358882101

 olivia@sdtuoda.com
olivia@sdtuoda.com  +86 13969540220
+86 13969540220